In modern industrial production, sealing technology is one of the key elements to ensure the safe and efficient operation of equipment. Whether in the fields of chemical engineering, machinery, or aerospace, gasket sealing technology plays an indispensable role. It not only effectively prevents the leakage of media, avoiding environmental pollution and resource waste, but also ensures the stable operation of equipment and extends its service life. Therefore, for engineering and technical personnel, it is crucial to have a deep understanding of the classification, selection, and application of gasket sealing technology, as well as its development trends.
There are numerous types of sealing technologies. Based on the angle between the sealing stress and the bolt load, they can be broadly divided into three categories: axial sealing, radial sealing, and inclined sealing. Each of these sealing methods has its own characteristics and is suitable for different application scenarios.
Axial sealing are a very common type of sealing method. The core feature of axial sealing is that the direction of the sealing stress is completely aligned with the direction of the bolt load. This type of seal is widely used in practical applications, with the most typical example being flange gasket sealing.
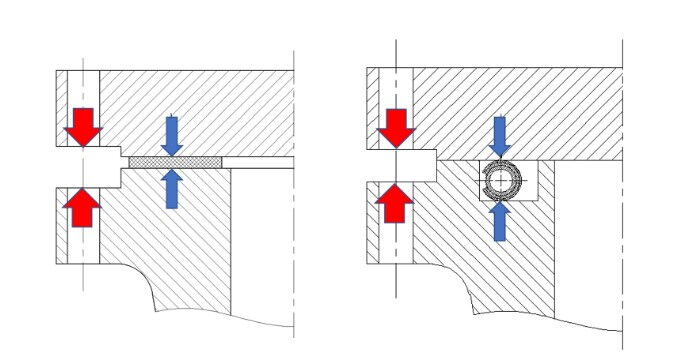
The principle of flange gasket sealing is relatively simple but highly effective. In industrial piping and equipment, flanges are essential components for connecting two parts. By placing gasket material between flanges, the gasket undergoes compression and deformation when the bolts are tightened, thereby achieving a seal. The load determination for this type of seal is relatively complex and will be discussed in detail later.
Axial sealing have several advantages, including simple structure, easy installation, and stable sealing performance. Due to their simple structure, the installation process is relatively straightforward and does not require complex tools or equipment. Moreover, the sealing performance of this type of seal is relatively stable under normal operating conditions, effectively preventing media leakage.
Radial sealing refer to sealing where the direction of the sealing stress is perpendicular to the direction of the bolt load. This type of seal plays a significant role in devices such as valves and pumps. Typical applications of radial sealing include stem packing sealing and radial sealing using C-rings or O-rings.
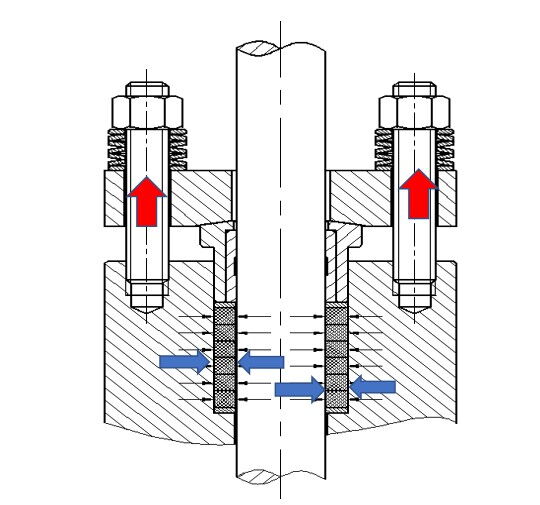
Stem packing sealing are a common form of radial sealing. In this type of seal, packing is placed around the valve stem, and an axial load is applied through a gland to cause the packing to deform, thereby creating a radial sealing stress. This stress effectively prevents media leakage and ensures the tight closure of the valve.
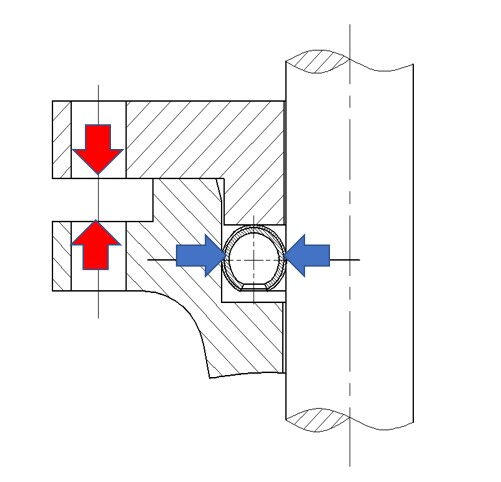
Radial sealing using C-rings or O-rings are another commonly used type of radial seal. This type of seal primarily relies on the elastic deformation of the ring to achieve sealing. Between the high-pressure side and the low-pressure side, the ring undergoes radial deformation due to the pressure difference, forming a sealing barrier to prevent media leakage. However, the inherent sealing stress of this type of seal is not very high, and its effectiveness may be compromised under high-pressure differences. However, through special design, it can be made into a self-tightening seal, widely used for sealing between high and low-pressure chambers in steam turbines, multi-stage pumps, and other applications.
Inclined sealing are a special type of seal where the direction of the sealing stress forms a certain angle with the direction of the bolt load. This type of seal has good adaptability and leakage prevention performance, making it particularly suitable for harsh environments such as high temperatures, high viscosity, and high corrosivity.
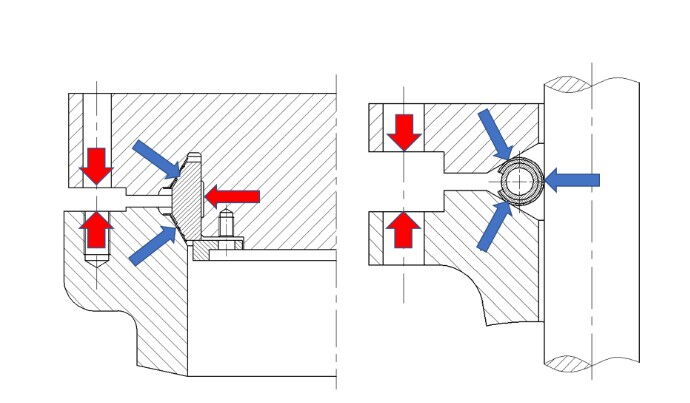
A typical application of inclined sealing is the ball valve seat seal. The ball valve seat seal utilizes the special structure between the ball valve seat and the ball, causing the sealing material to undergo compression and deformation during the opening and closing of the valve, thereby achieving a seal. This type of seal not only has good sealing performance but also a longer service life.
In addition to ball valve seat sealing, inclined sealing also include special forms such as double-cone ring gaskets, octagonal gaskets, elliptical gaskets, and lens gaskets. Each of these sealing forms has its own characteristics and is suitable for different application scenarios.
In practical engineering, selecting the appropriate sealing method is crucial for ensuring the efficient operation of equipment. Different sealing methods are suitable for different application scenarios, so when choosing sealing technology, it is necessary to consider a variety of factors, including the working environment of the equipment, the nature of the media, and the pressure and temperature conditions.
Working Environment: The selection of sealing technology must take into account the working environment of the equipment. For example, in harsh environments such as high temperatures, high viscosity, and high corrosivity, inclined sealing may be more suitable due to their good adaptability and leakage prevention performance.
Nature of the Media: The nature of the media is also an important factor in selecting the sealing method. Different media have different requirements for sealing materials. For example, corrosive media may require special corrosion-resistant materials.
Pressure and Temperature Conditions: The pressure and temperature conditions during equipment operation also affect the selection of the sealing method. For example, under high-pressure differences, C-rings or O-rings used in radial sealing may require special design to meet the requirements.
In practical applications, the selection and application of sealing technology need to be adjusted according to specific circumstances. For example, in industrial piping, flange gasket sealing are a common type of axial seal suitable for most conventional environments. In devices such as valves and pumps, radial and inclined sealing are more common because they can better meet the special needs of these devices.
With the continuous development of engineering technology, sealing technology is also constantly evolving. Modern sealing technology not only demands higher sealing performance but also requires better adaptability and reliability. For example, the development of self-tightening sealing technology has significantly improved sealing effectiveness under complex conditions such as high-pressure differences.
Moreover, the development of new sealing materials also provides support for the progress of sealing technology. These new materials not only have better corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance but also meet the sealing requirements under special conditions.
Sealing technology plays a vital role in engineering technology. By understanding the direction of sealing stress and the characteristics of sealing methods, we can better select and apply sealing technology to ensure the normal operation of equipment and the safe transportation of media. Whether it is axial sealing, radial sealing, or inclined sealing, each type of seal has its unique advantages and applicable scope. In practical engineering, the rational selection and application of sealing technology are the keys to ensuring the efficient operation of equipment.
In summary, sealing technology is an indispensable part of engineering technology. Through continuous research and innovation, we can further improve the performance and reliability of sealing technology, providing solid support for the development of engineering technology.