In modern industrial operations, spanning sectors such as petroleum, chemical processing, metallurgy, power generation, shipbuilding, and machinery manufacturing, sealing has always been a critical engineering concern. Equipment like pipelines, valves, pressure vessels, and other process components require effective sealing to ensure safe operation, prevent environmental contamination, and maintain optimal production efficiency. Failures in sealing can have severe consequences, ranging from equipment damage and production interruptions to safety hazards and environmental pollution. Among the numerous sealing solutions available, spiral wound gaskets have emerged as a leading choice due to their unique construction, superior performance, and adaptability to diverse industrial conditions. Spiral wound gaskets have become a preferred sealing element in a variety of challenging applications, providing engineers with a reliable solution where both performance and safety are paramount.
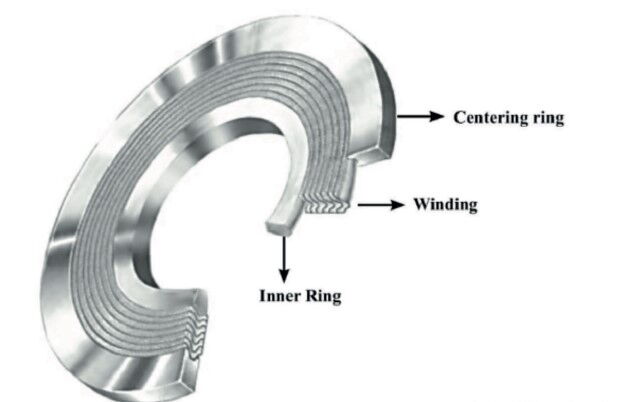
A spiral wound gasket is a semi-metallic gasket, meticulously constructed by alternately winding high-quality stainless steel strips and soft filler materials. Common stainless steel types include SUS304 and SUS316, and the strips are usually formed in a “V” or “W” cross-sectional shape to enhance elasticity and sealing reliability. Soft filler materials, which are layered between the metal strips, can include graphite, asbestos, PTFE, or other non-asbestos alternatives. This combination of metal and soft material, arranged in alternating spiral layers, forms a gasket that is both resilient and highly effective in sealing applications.
To ensure the structural stability of the gasket, the metal strips at both the start and end of the winding are typically secured using spot welding. The basic type of spiral wound gasket does not include inner or outer rings, making it suitable for medium- and low-pressure applications involving tongue-and-groove flanges, flat flanges, or raised face flanges. The primary sealing mechanism relies on the elastic deformation of the metal strips and the compressibility of the filler material. Under compressive forces applied during flange tightening, the metal strips deform elastically while the soft filler material fills microscopic gaps on the flange surfaces. This creates a highly effective seal that can adapt to minor imperfections on the flange face.
The V- or W-shaped metal strips provide multi-level structural reinforcement, similar to V-shaped packing. By stacking layers in this manner, the gasket achieves both high mechanical strength and excellent sealing reliability, effectively preventing leakage of process media under various operating conditions.
- Excellent Compression and Recovery: One of the key advantages of spiral wound gaskets is their outstanding compressibility and recovery. During flange assembly, when the tightening force is applied, the gasket compresses evenly, filling tiny gaps and imperfections between the flange sealing surfaces. Once the pressure is released, the gasket recovers partially, maintaining its shape and ensuring long-lasting sealing performance. This characteristic allows spiral wound gaskets to adapt to minor flange surface defects, making them highly tolerant of small irregularities and ensuring continued sealing integrity.
- Multi-Layer Sealing and Self-Tightening Function: The alternating arrangement of metal strips and filler material creates multiple sealing barriers, which effectively form a multi-layer sealing mechanism. When process pressure acts on the gasket, each layer resists the media to a certain extent, resulting in multiple barriers that prevent leakage. Additionally, spiral wound gaskets have a self-tightening capability. Under operational pressure, the gasket compresses further, enhancing the seal. This is particularly beneficial in applications with fluctuating pressures, such as steam systems, chemical reactors, or high-pressure pipelines, where the risk of leakage is increased. The self-tightening feature ensures that even under dynamic conditions, the gasket maintains a reliable seal.
- Adaptability to Harsh Conditions: Spiral wound gaskets are engineered to perform reliably under extreme industrial conditions, including high and low temperatures, high vacuum, cyclic vibration, and shock loading. This resilience is a result of the synergistic combination of metal strips and soft filler materials. The metal component provides mechanical strength and dimensional stability, allowing the gasket to retain its shape under high pressure and elevated temperatures. Simultaneously, the filler material imparts flexibility and adaptability, enabling the gasket to accommodate thermal expansion, contraction, and mechanical vibrations.
For example, in the petroleum and chemical industries, pipelines may carry high-temperature, high-pressure fluids, sometimes in highly corrosive environments. In such applications, the spiral wound gasket reliably prevents leakage, protecting both personnel and equipment. In shipbuilding or aerospace applications, where high vacuum conditions and vibration are common, these gaskets maintain performance integrity, ensuring operational safety and reducing maintenance requirements. This combination of durability, adaptability, and resilience underscores the gasket’s suitability for a wide range of industrial conditions.
Spiral wound gaskets are utilized extensively across multiple industries due to their exceptional sealing capabilities. In the petroleum industry, they seal pipelines, valves, and pressure vessels, preventing leaks that could lead to environmental contamination and production losses. During extraction, transport, and refining processes, spiral wound gaskets ensure the containment of hydrocarbons, reducing safety risks and protecting the surrounding environment.
In the chemical industry, spiral wound gaskets are essential for handling corrosive substances. By selecting appropriate filler materials such as PTFE, gaskets resist chemical attack, ensuring consistent and safe chemical processing. Similarly, in metallurgy, high-temperature equipment requires gaskets that can withstand extreme heat without losing integrity. Spiral wound gaskets are capable of maintaining effective sealing in such environments, ensuring uninterrupted metallurgical operations.
Other industries, including power generation, shipbuilding, natural gas, nuclear energy, aerospace, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and mechanical engineering, also benefit from spiral wound gaskets. They are commonly employed in flange connections for condensers, heat exchangers, towers, manholes, and handholes. Across all these applications, spiral wound gaskets provide a reliable seal, protecting equipment and enhancing operational safety.
Spiral wound gaskets are classified based on the presence of inner and outer rings into four main types: basic type, inner ring type, outer ring type, and inner-outer ring type.
- Basic Type: Simple in design, easy to install, suitable for grooved flanges.
- Inner Ring Type: Designed for embedded flanges; the inner ring reinforces sealing and prevents erosion by the media.
- Outer Ring Type: Suitable for flat flanges; the outer ring ensures correct positioning during installation.
- Inner-Outer Ring Type: Provides the highest strength, suitable for flat flanges under high pressure or complex operating conditions.
The choice of gasket type is determined by flange design and operational requirements. For example, in high-pressure flat flange connections, the inner-outer ring type is typically preferred to ensure maximum sealing reliability.
Material Selection:
- Metal Strip (Hoop): Commonly SUS304 or SUS316L. For high-performance applications, specialty alloys like titanium or Inconel may be used.
- Filler Material: Expanded graphite is versatile, suitable for steam and non-corrosive media. PTFE offers superior corrosion resistance and is ideal for acidic or alkaline chemicals. Inorganic fillers are cost-effective but provide moderate performance.
- Rings (Reinforcement): Carbon steel is suitable for general utility applications, whereas stainless steel is preferred for corrosive media in process pipelines.
Engineers select gasket materials based on media type, temperature, pressure, and flange configuration, ensuring optimal sealing performance for each specific application.
- Preparation Before Installation: Ensure flange sealing surfaces are clean, smooth, and undamaged. Any debris, corrosion, or surface irregularities can compromise sealing. Select the appropriate gasket size and type for the flange and operating conditions. For gaskets with positioning rings, verify that they are intact to facilitate proper placement during installation.
- Installation Considerations: Position the gasket accurately on the flange, ensuring correct alignment. For gaskets with inner and outer rings, pay close attention to proper placement to avoid installation errors. Bolt tightening should follow a symmetrical pattern to ensure even compression. Over-tightening or uneven tightening can negatively affect sealing performance. Follow recommended torque specifications based on gasket material and operating conditions to achieve uniform stress distribution and optimal sealing.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Periodically inspect flange connections during operation to check for leaks. If leakage is detected, investigate the cause and take corrective action immediately. For equipment in continuous operation, gaskets should be replaced according to maintenance schedules to ensure reliable sealing. During gasket replacement, inspect the flange surfaces carefully and repair or replace damaged surfaces to maintain sealing integrity.
Compared with conventional rubber gaskets, spiral wound gaskets offer superior resistance to high pressure and temperature. Rubber gaskets tend to age, deform, or crack under extreme conditions, leading to seal failure. In contrast, spiral wound gaskets, reinforced with metal strips, can maintain long-term performance in demanding applications.
When compared to PTFE gaskets, which are highly corrosion-resistant but prone to extrusion under high pressure, spiral wound gaskets provide superior stability and resistance. Their metal reinforcement allows them to withstand high-pressure environments without compromising sealing performance, making them highly reliable for high-pressure gas pipelines, steam systems, and hazardous chemical installations.
Spiral wound gaskets, with their unique construction, exceptional sealing performance, and wide applicability, are an indispensable component in industrial sealing. Proper selection of gasket type and materials, combined with adherence to recommended installation and maintenance procedures, ensures safe and reliable operation. As technology advances and industrial processes evolve, spiral wound gaskets will continue to play a critical role, providing robust, long-lasting protection across a diverse range of industries. Their proven performance, adaptability, and reliability make them a cornerstone in the field of industrial sealing, offering engineers a dependable solution for critical equipment and processes.